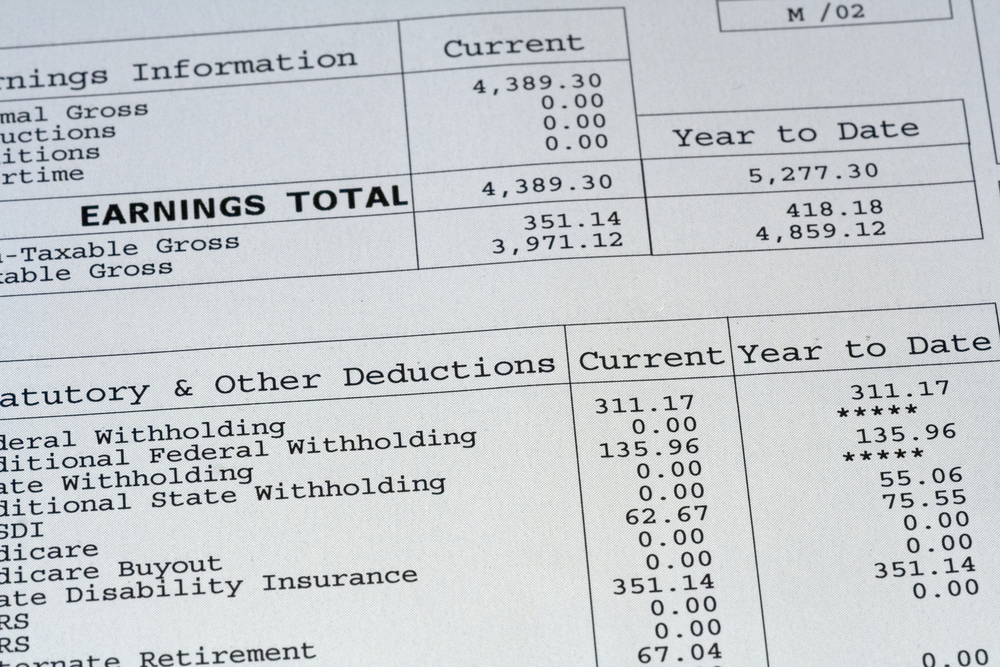
The EEOC has been ordered to collect employers’ EEO-1 Component 2 pay data by September 30, 2019. The D.C. District Court issued the order after finding back in March 2019 that Office of Management and Budget (OMB’s) decision to stay the collection of Component 2 pay data lacked the reasoned explanation required by the Administrative Procedure Act. See our prior blog posts here, here, and here about National Women’s Law Center v. Office of Management and Budget, No. 17-cv-2458 (TSC) (D.D.C.). Since then the court has been critical of the EEOC’s compliance with its order, and held a status conference and a hearing in March and April. READ MORE
District Court Orders Employers to Submit Component 2 Data by September 30, 2019